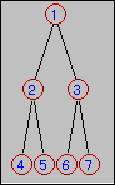
Figure 1:A binary tree.



Let us now consider how to draw the binary tree depicted in Figure 1.

We first define a class, called Node, for the nodes.
class Node {
component Label lb;
component Circle circle;
attribute int x == circle.centerX;
attribute int y == circle.centerY;
inside(lb,circle);
}
There are two components: a label and a circle. The constraint
inside(lb,circle) ensures that the label must lie inside the circle.
The two attributes x and width are introduced to make it
easier to relate one node with others.
We then define a class, called Tree3, for binary trees that have three nodes, one being the root and the other two being the leaves.
class Tree3 {
component Node root,lc,rc;
component Line l1,l2;
symmetric(root,lc,rc);
leftto(lc,rc);
connect(l1,root,lc);
connect(l2,root,rc);
}
A Tree3 object is composed of three nodes and two lines. The
constraint symmetric(root,lc,rc) says that the two leaves
lc and rc must be symmetric to the root; the constraint
leftto(lc,rc) says that node lc must be placed to the left of
rc; and the constraint connect(l1,root,lc) ensures that
the line l1 connects the node root and node lc.
This constraint symmetric is defined as follows:
constraint symmetric(Node root, Node lc, Node rc){
root.x == (lc.x + rc.x)/2;
lc.y == rc.y;
root.y == rc.y-50;
}
must be symmetric to the root; the second one says that the two leaves
must have the same y-coordinate; and the last one says that the root
must be 50 points higher than the two leaves.
Now, we are ready to build the tree depicted in Figure 1 by combining the parts already available.
Class Tree {
component Tree3 t1{root.lb.text=="1";lc.lb.text=="2";rc.lb.text=="3"};
component Tree3 t2{root == t1.lc;lc.lb.text=="4";rc.lb.text=="5"};
component Tree3 t3{root == t1.rc;lc.lb.text=="6",rc.lb.text=="7"};
leftto(t2.rc,t3.lc);
}


